 Long wave infrared (LWIR) cameras are a common form of thermal imaging used in industrial applications. While there are other types of infrared imaging, chances are if you need thermal imaging, you’ll need a LWIR cameras.
Long wave infrared (LWIR) cameras are a common form of thermal imaging used in industrial applications. While there are other types of infrared imaging, chances are if you need thermal imaging, you’ll need a LWIR cameras.
But what exactly are LWIR cameras? How do they work and what are they typically used for?
What is a LWIR Camera and How Does it Work?
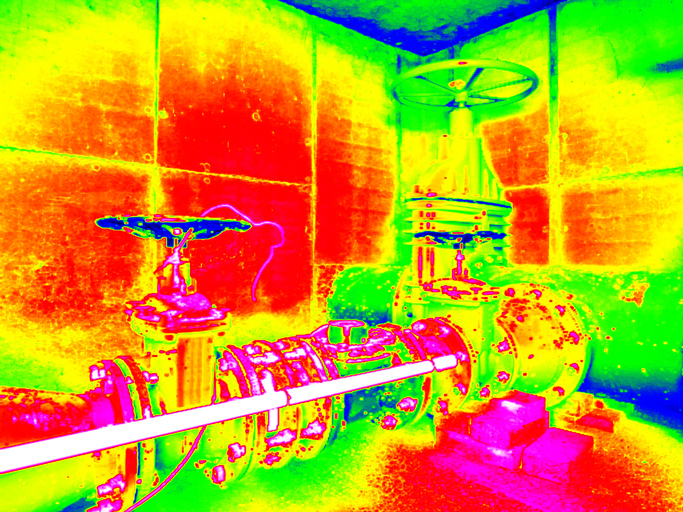
LWIR cameras capture light in the 8 -14 μm spectral band. This is opposed to short wave infrared cameras that operate in the 0.9 - 1.7 μm spectral band, and medium wave infrared cameras that operate in the 3 - 5 μm spectral band.
Typically, LWIR cameras leverage a bolometer or microbolometer as an image sensor. These are usually made of amorphous silicon (a-Si) or Vanadium Oxide (VOx) and are uncooled – older versions of thermal imaging required a cooling system for accurate imaging, but bolometers and microbolometers changed this. Each type of sensor and material has their various benefits – but they all must use a germanium lens to allow infrared light to pass through.
What are LWIR Cameras Used For?
LWIR cameras can detect light invisible to the naked eye in the infrared spectrum. The resulting applications are numerous and varied. Some of the most common include:
- Thermography
- Temperature control
- Predictive maintenance
- Gas leak detection
- Broad dynamic range environments
- Imaging through thick smoke
For applications like gas leak detection or imaging through thick smoke, LWIR cameras give us a glimpse into environments, sometimes potentially dangerous ones, where we would otherwise be unable to detect anything.
LWIR cameras are practical for a number of applications in the industrial sector. They’re a common type of thermal imaging, though the cameras themselves can come in many different forms and performance levels.
To learn more about common LWIR cameras, check out Dalsa’s Caliber LWIR cameras from Phase 1 Technology.
